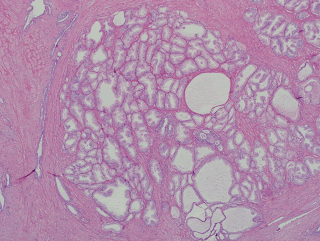
*BPH ; has a nodular microcystic appareance, tiny cysts epresenting dilated hyperplastic prostatic asini.(1)
*The earliest BPH nodules are predominantly stromal and are composed mainly of fibrous tissue admixed with some smooth muscle and more numerous BPH nodules are typically more situated within the transition zone. (2)
 |
| http://www.cap.org/apps/docs/reference/myBiopsy/prostate_benign.html |
*Benign needle biopsy specimens of the prostate should be diagnosed as “benign prostate tissue,” not as “benign prostatic hyperplasia.” First, many needle biopsy specimens do not even sample the transition zone. Second, histologic findings on needle biopsy, with the exception of stromal nodules, do not correlate with size of the prostate or urinary obstructive symptoms . Finally, signing out a specimen as “BPH” may falsely reassure the urologist that a palpable or hypoechoic lesion of concern has been sampled.(2)
*Within areas of BPH, nodules or a diffuse stromal infiltrate of
lymphocytes and plasma cells are commonly seen in a peri-glandular distribution.
However, in the majority of cases these findings have not been identified with
an infectious process or clinical symptoms of prostatitis. (2)
*Prostatic infarcts can be found in approximately 20% to 25% of specimens removed for BPH and immediately adjacent to the infarcts, reactive epithelial nests with prominent nucleoli, some pleomorphism, and even atypical mitotic figures can be seen, mimicking urothelial or squamous cell carcinoma. Progressing away from the center of the infarct, more mature squamous metaplasia is seen. (2)
*(1) Functional Histology-A Text And the Colour Atlas - P.R.Wheather
*(2) Sternberg's Diagnostic Surgical Pathology, 5th Edition




Hiç yorum yok:
Yorum Gönder